Since Attention mechanism was proposed, the seq2seq model with attention has been improved in each task, so the current seq2seq model usually refers to the model combining RNN and Attention. The specific models can refer to previous posts. After then, Google proposed a transformer model to solve the seq2seq problem, replacing the LSTM with a full attention structure and achieved better results in the translation task. This post will focus on Attention is All You Need.
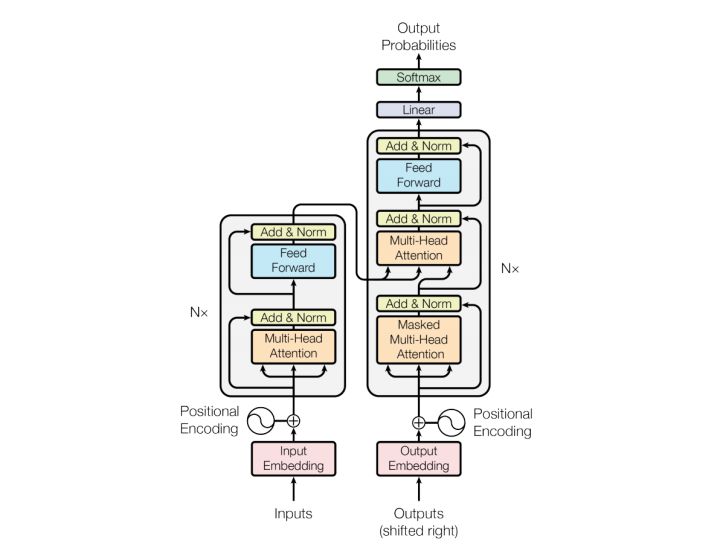
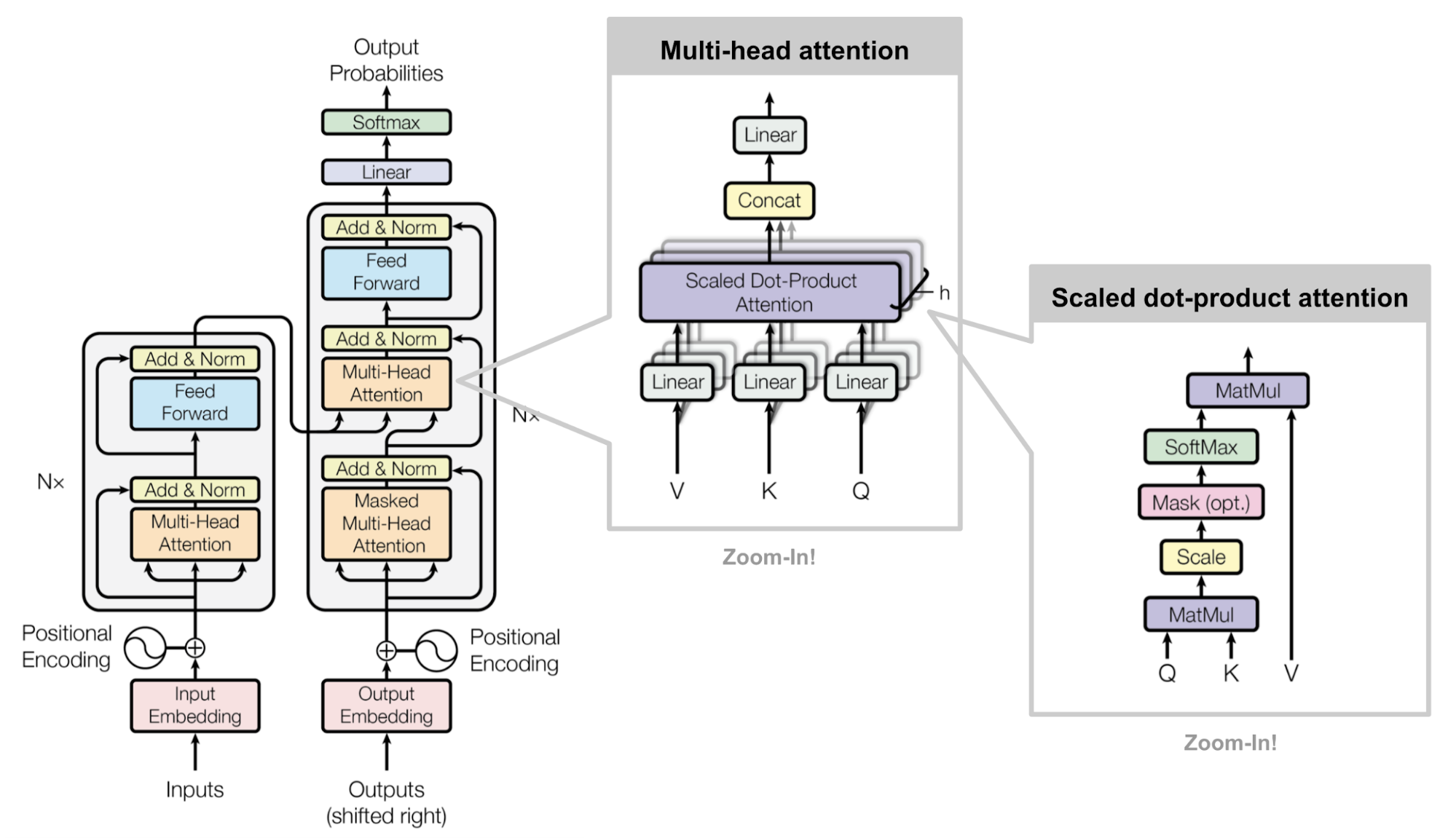
Same as most seq2seq model, transformer also consists of Encoder and Decoder.
Encoder
Encoder consists of N = 6 identical layers. The layer refers to the unit on the left side of the model figure. There is an Nx on the left, here is *6. Each layer consists of two sub-layers: a multi-head self-attention mechanism and a fully connected feed-forward network. Each sub-layer adds a backup connection and normalization, so the output of the sub-layer can be expressed as:
Key, Value and Query
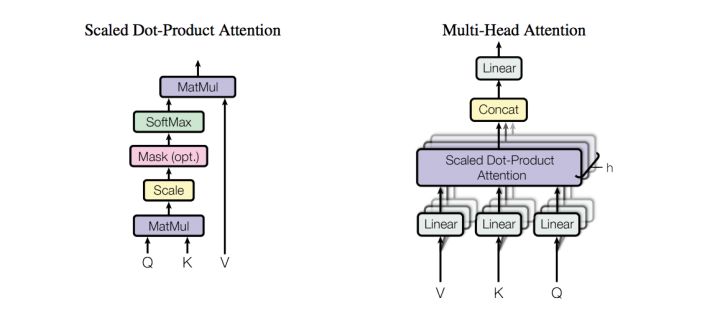
The major component in the transformer is the unit of multi-head self-attention mechanism. The transformer views the encoded representation of the input as a set of key-value pairs, (K, V), both of dimension n (input sequence length); in the previous output is compressed into a query (Q of dimension m) and the next output is produced by mapping this query and the set of keys and values.
Multi-head Self-Attention
Attention can be expressed as:
Multi-head attention is the project Q, K V through h different linear transformations, and finally splicing different attention results:
In self-attention, Q, K, V are set same.
In the paper, they use scaled dot-product to calculate attention:
Position-wise Feed-forward Network
Decoder
The structure of Decoder and Encoder are similar, but there is an additional sub-layer of attention. Here we first define the input, output and decoding process of the Decoder:
- Output: probability distribution of output words corresponding to ith position;
- Input: output of Encoder and output of Decoder corresponding to (i - 1)th position. Hence, the intermediate attention is not self-attention, the K, V come from the Encoder while Q comes from the output of the previous position Decoder.
- Decoding: here we need to pay special attention to the fact that the encoding can be calculated parallel, all encoded at once; however, the decoding does not solve all sequences at once, but solves them one by one just like RNN. Because the input of the previous position is used as the Query of attention.
Positional Encoding
In addition to the Encode and Decoder, there are also data preprocessing parts. Transformer discards RNN, while the biggest advantage of RNN is the abstraction of data in time series. Hence, the author proposes two methods of Positional Encoding, which sums the encoded data with the embedding data with relative position information.
- Method 1: directly calculate with sin and cos functions with different frequencies
- Method 2: learn a positional embedding
They both give the same results, so we list first method as follows:
- Any position of PE_{pos+k} can be represented by a linear function of PE_{pos};
Full Architecture
We can summarize the full architecture as follows:
- both the source and target sequences first go through embedding layers to produce data of the same dimension;
- to preserve the position information, we applied positional encoding using sin and cos function with different frequencies;
- we apply a softmax and linear layer to the final decoder output.