Attention is a mechanism for improving the effects of the RNN (LSTM or GRU) based Encoder + Decoder model, commonly referred to as the Attention Mechanism. Attention Mechanism is very popular at present, widely used in many fields such as machine translation, speech recognition, image caption, etc. It is so popular because Attention gives the model the ability to distinguish between regions, for example, in machine translation, speech recognition applications, each word in a sentence is given different weights, making the learning of the neural network model more flexible, and Attention itself can be used as an alignment relationship to interpret translation between input/output sentences. Hence, attention in deep learning can be viewed as a vector of importance weights: we estimate or classify using the attention vector how strongly it is correlated with other elements and take the sum of their values weighted by the attention vector as the approximation of the target.
Two problems Attention Mechanism Solves
Seq2seq introduces a model based on an Encoder and a Decoder to build a neural network based end-to-end machine translation model, in which, Encoder encodes the input X in a fixed-length hidden vector Z and Decoder decodes the target output Y based on the hidden vector Z. This is a classic seq2seq model, but there are two obvious problems:
-
Compress all information of input X to a fixed length of hidden vector Z while ignoring the true length of X, will result in the sharp decline of performance especially when the length of input X is longer than initial lengths from training dataset.
-
It is unreasonable to encode the input X into a fixed length and give the same weight to each word in the sentence. For example, in machine translation, between input sentence and the output sentence, one or several words usually correspond to one or several words. Hence, each word entered given the same weight does not provide discrimination.
Hence, this fixed-length context vector design will lead to a critical and apparent disadvantage that is incapability of remembering long sentences. Often it has forgotten the first part once it completes processing the whole input. Now, it’s time to introduce Attention that resolves the above problems.
Attention Mechanism
The attention mechanism was born to help memorize long source sentences in neural machine translation. The secret sauce invented by attention is to create shortcuts between the context vector and the entire source input. The weights of these shortcut connections are customizable for each output element.
In the paper, they construct the following architecture with three pieces of information:
- encoder hidden states;
- decoder hidden states;
- alignment between source and target;
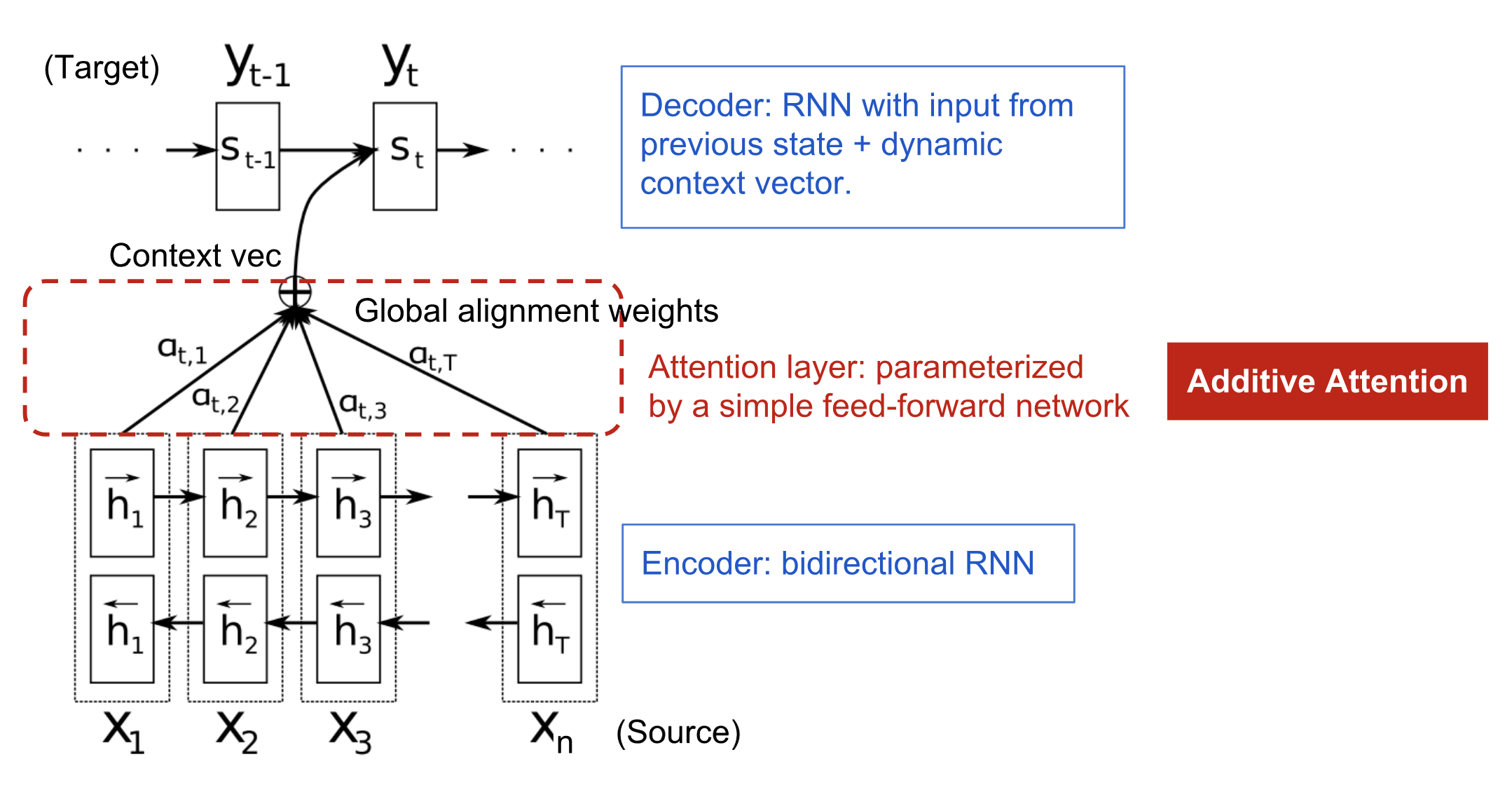
In the model, they define a conditional probability:
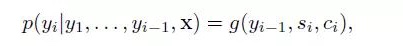
where, si is the hidden state from RNN in decoder:
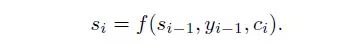
Here ci is a weighted value, defined as:
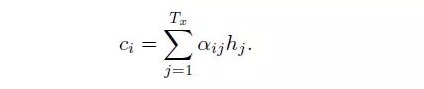
where i is the ith word from encoder, hj is the jth hidden vector from encoder, aij is the weighted value between jth word from encoder and ith word from decoder, indicating the effect from jth word from source to ith word in target. aij is calculated as:
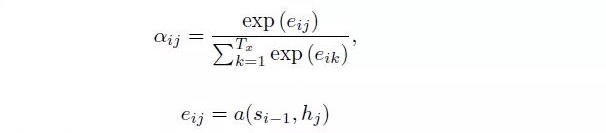
Here, aij is the softmax output, with the summation equal 1. eij represents the alignment, to estimate the alignment effect from jth word from encoder to ith word from decoder. There are different alignment score functions, and the basic one is defined as follows, known as dot product, i.e., dot product between hidden state from target output and hidden state from source output.
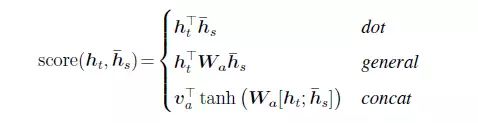
Different Types of Attention Mechanism
Self-Attention
Self Attention is very different from the traditional Attention mechanism: the traditional Attention is based on the source and target hidden states to calculate Attention, and the result is the dependence between each word at the source and each word at the target. However, for self Attention, it is performed on the source and target sides respectively, and only use the Self Attention associated with the source input or the target input itself to capture the dependency between the source and the target itself. Then it adds the self Attention from the source to the self Attention from the target to capture the relationship between the source and the target. It has been shown to be very useful in machine reading, abstractive summarization, or image description generation.